Decisions are an inevitable part of life, whether in personal matters or professional settings. However, when faced with complex situations or multiple options, making the right choice can be challenging. This is where decision charts/decision trees come in, offering a visual representation of decision-making processes that can guide individuals and organizations towards better outcomes.
What is a Decision Chart?
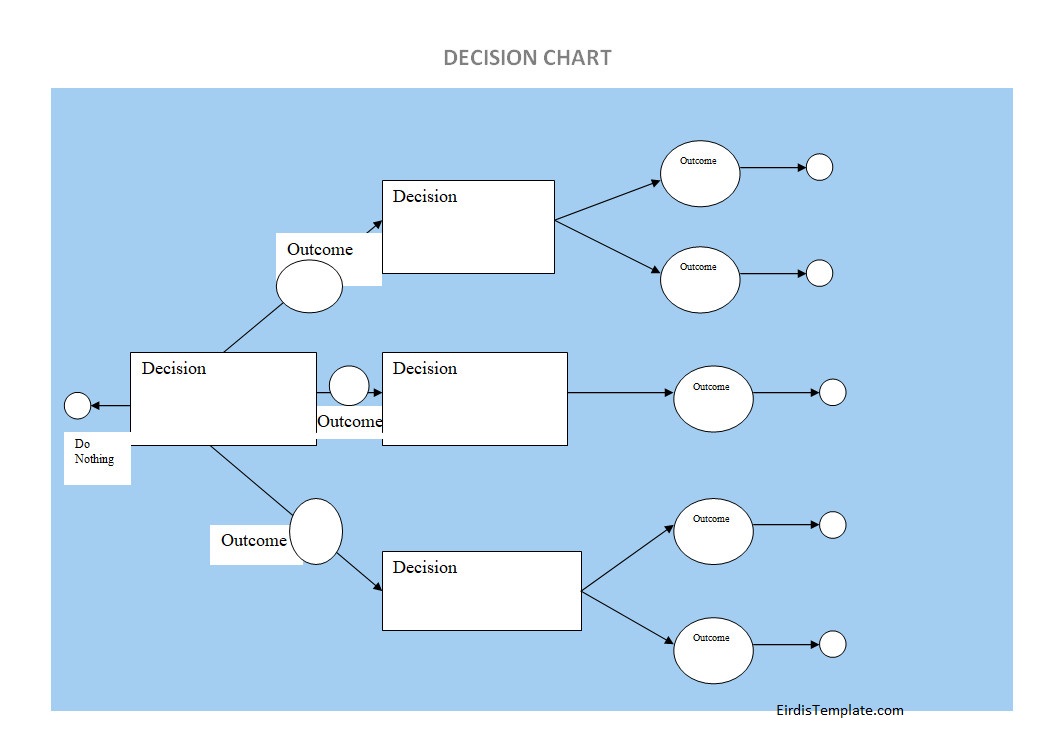
A decision chart is a visual tool used to map out choices and their possible outcomes. It breaks complex decisions into clear steps, using branches to show different options and results. By organizing decisions in this way, it helps individuals or teams compare alternatives, weigh risks, and choose the best course of action with greater confidence and clarity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
1. Advantages of Decision Charts
Decision charts offer several advantages that make them invaluable tools for decision-making processes. One of the key benefits of decision charts is the clarity they provide in complex situations. By visually representing choices and outcomes, decision charts make it easier for users to understand the implications of different decisions and weigh their options. The structured framework of decision charts helps users analyze scenarios systematically, leading to more informed and strategic decision-making. Additionally, decision charts promote collaboration and communication among team members by providing a shared visualization of the decision process.
Decision charts also offer flexibility, allowing users to modify and update the chart as new information becomes available. This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments where decisions need to be adjusted based on changing circumstances. Furthermore, decision charts promote efficiency by streamlining decision-making processes and saving time and resources. By following a structured framework and considering various outcomes, users can make decisions more efficiently and effectively, leading to better results in the long run.
2. Disadvantages of Decision Charts
While decision charts offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain limitations and challenges. One of the main disadvantages of decision charts is their potential complexity, especially in situations with multiple decision points and outcomes. Creating and interpreting complex decision charts can be time-consuming and may require specialized knowledge or expertise. Moreover, decision charts are based on assumptions and probabilities, which can introduce subjectivity and bias into the decision-making process.
Another limitation of decision charts is their inherent limitations in accounting for all possible outcomes or factors. Decision charts rely on the information available at the time of creation, which may not capture unforeseen events or changes in circumstances. This can lead to oversimplified decision-making or overlooking important considerations that could impact the outcome. Despite these challenges, decision charts remain valuable tools for structuring decision-making processes and providing a visual guide for weighing options and consequences.
When to Use a Decision Chart?
1. Decision-Making Scenarios
Decision charts are most beneficial in situations where there are multiple options to consider, each with distinct consequences or uncertainties. They are particularly useful when organizations or individuals need to make strategic decisions that have significant implications for the future. Decision charts can help in weighing alternatives, analyzing risks, and planning for different scenarios, making them versatile tools for navigating complex decision-making scenarios. Whether it’s choosing between different investment opportunities, evaluating healthcare treatment options, or planning project milestones, decision charts can provide a structured approach to decision-making.
2. Strategic Planning
In strategic planning processes, decision charts play a crucial role in aligning organizational goals with actionable strategies. By visualizing different courses of action and their potential outcomes, decision charts help leaders and teams make informed decisions that support long-term objectives. Strategic planning often involves evaluating multiple scenarios, considering various factors, and anticipating future trends. Decision charts provide a visual representation of these considerations, enabling stakeholders to collaborate, prioritize initiatives, and allocate resources effectively.
3. Risk Management
Decision charts are also valuable tools in risk management processes, where organizations need to assess potential risks, uncertainties, and mitigating strategies. By mapping out different risk scenarios and their consequences, decision charts help identify high-risk areas, prioritize risk mitigation efforts, and develop contingency plans. Risk management involves analyzing the likelihood and impact of various risks on business operations and making decisions to minimize potential losses. Decision charts provide a structured framework for risk assessment and decision-making, enabling organizations to proactively manage risks and protect their interests.
4. Data Analysis
In data-driven decision-making processes, decision charts can help organizations analyze complex data sets, identify patterns, and make informed choices based on data insights. By visualizing data points, trends, and correlations, decision charts enable users to interpret information more effectively and draw meaningful conclusions. Data analysis often involves processing large volumes of data, performing statistical analysis, and deriving actionable insights to support decision-making. Decision charts provide a visual representation of data analysis results, making it easier for users to understand trends, relationships, and potential outcomes.
5. Process Improvement
Decision charts can also be used in process improvement initiatives to optimize workflows, streamline operations, and enhance efficiency. By visualizing the sequence of steps in a process, decision charts help identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. Process improvement involves analyzing existing processes, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing changes to increase productivity and quality. Decision charts provide a visual roadmap for process improvement efforts, guiding teams through the steps needed to achieve desired outcomes and drive continuous improvement.
How to Draw a Decision Chart
1. Identifying Decision Points
The first step in drawing a decision chart is to identify the key decision points that need to be made. Decision points are critical junctures in the decision-making process where choices need to be evaluated and selected. By clearly defining decision points, users can map out the decision-making process and determine the options available at each stage.
2. Defining Options
Once the decision points have been identified, the next step is to define the options or choices available for each decision point. Options represent the different paths that can be taken based on the decisions made at each stage. By outlining the various options, users can visualize the potential outcomes and consequences of each choice.
3. Mapping Outcomes
After defining the options, the next step is to map out the potential outcomes or consequences associated with each choice. Outcomes represent the results or implications of selecting a particular option at a decision point. By linking options to outcomes, users can understand the cause-and-effect relationships between decisions and their consequences.
4. Connecting Nodes
Once the decision points, options, and outcomes have been defined, the next step is to connect the nodes in the decision chart. Nodes represent decision points, options, and outcomes, and branches represent the connections between them. By drawing branches between nodes, users can visualize the flow of decisions and outcomes in the decision-making process.
5. Adding Probabilities
In some decision charts, probabilities may be assigned to each outcome to reflect the likelihood of that result occurring. Probabilities help users assess the level of risk associated with each option and make informed decisions based on the potential outcomes. By incorporating probabilities into the decision chart, users can consider the likelihood of different scenarios and plan accordingly.
6. Reviewing and Refining
Once the decision chart has been drawn, it is essential to review and refine it to ensure accuracy, clarity, and completeness. Users should double-check the chart for any errors, inconsistencies, or missing information. By refining the decision chart, users can ensure that it accurately represents the decision-making process and provides a clear visualization of the options and outcomes available.
Decision Chart Template
Start using our free decision chart template today to evaluate options clearly, compare outcomes, and make confident, well-informed decisions.
Decision Chart Template – Word
- Free Printable Monthly Expenses Template - February 12, 2026
- Printable Monthly Employee Schedule Template - February 11, 2026
- Printable Monthly Budget Planner Template - February 10, 2026